Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by the darkening of certain areas of the skin due to an excess production of melanin. While it is not harmful, it can be a source of discomfort and self-consciousness for many individuals. Understanding the causes, types, and available treatments for hyperpigmentation is crucial for effective management and achieving clear, even-toned skin.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation:
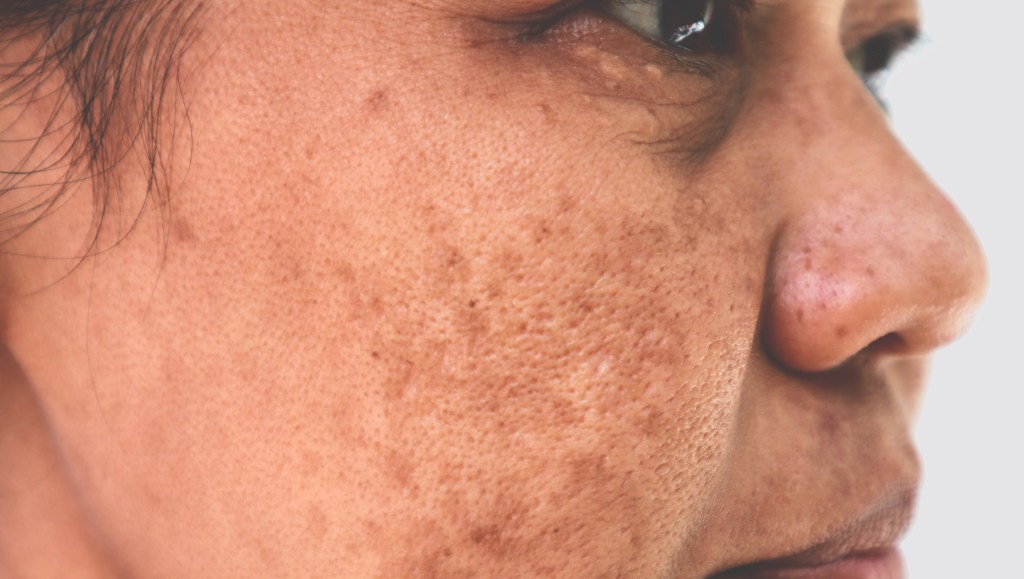
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and certain medications. UV radiation from the sun stimulates the production of melanin in the skin as a protective mechanism, leading to tanning or dark spots. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or while taking oral contraceptives can trigger melasma, a type of hyperpigmentation commonly seen as dark patches on the face. Inflammation resulting from acne, eczema, or injury can also lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Types of Hyperpigmentation:
Hyperpigmentation manifests in different forms, each with its own distinct characteristics. Melasma typically appears as symmetrical patches of brown or grayish pigmentation on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. Sunspots, also known as solar lentigines or liver spots, are flat, brown spots that develop on sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, and shoulders. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs as a result of trauma to the skin and presents as dark marks or spots following acne, cuts, or burns.
Treatment Options:
Effective management of hyperpigmentation involves a combination of preventive measures and targeted treatments tailored to the specific type and severity of the condition. Sun protection is paramount in preventing further darkening of the skin and minimizing the risk of new pigmentation. Broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF should be applied daily, along with wearing protective clothing and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
Topical treatments containing ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, azelaic acid, kojic acid, and vitamin C can help lighten existing pigmentation and inhibit melanin production. These products are available over-the-counter or may require a prescription for stronger formulations. Chemical peels and microdermabrasion treatments performed by dermatologists or trained professionals can exfoliate the skin and promote cell turnover, reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
In-office procedures such as laser therapy and intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments offer targeted and more aggressive approaches to addressing stubborn pigmentation. These procedures work by selectively targeting melanin in the skin, breaking it down and promoting its removal. Multiple sessions may be required to achieve desired results, and downtime and potential side effects should be discussed with a healthcare provider beforehand.
Home remedies and natural treatments, while popular, may offer limited efficacy and inconsistent results. Ingredients such as lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, and certain essential oils may cause irritation and worsen hyperpigmentation in some individuals. It is advisable to consult with a dermatologist before attempting any DIY remedies to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Conclusion:
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that can impact individuals of all skin types and ethnicities. Understanding the underlying causes and available treatment options is essential for effectively managing this condition and achieving a clearer, more even complexion. Sun protection, topical treatments, and in-office procedures are key components of a comprehensive approach to addressing hyperpigmentation. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on individual skin needs and concerns. With proper care and treatment, hyperpigmentation can be effectively managed, restoring confidence and promoting healthy skin.
Read more information here at https://purehnb.com/hyperpigmentation/.